Female Sexual and Reproductive System
Female Sexual Anatomy :
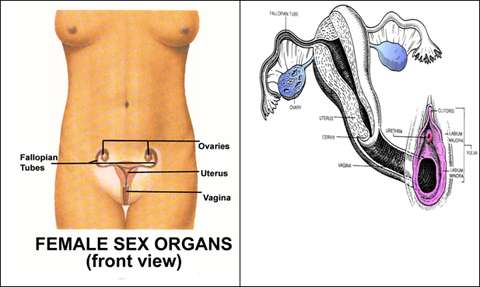
The female sexual organs consists of an external group called VULVA comprising 1)mons veneris 2)labia Majora 3)Labia Minora 4)Bartholin's glands 5)Hymen 6)Clitoris. The internal group is enclosed and protected in pelvic cavity comprises of 1)Vagina 2)Uterus 3)Fallopian tubes 4)Ovaries.
Mons Veneris : is a rounded mass of fat at the lower end of abdomen in front of Symphysis pubis.
Labia Majora : or outer or large lips are two longitudinal folds which begin at Mons veneris. They have hair growth and sweat glands. They protect the inner organs.
Labia Minora : or inner or small lips are like curving petals. Visible only if outer lips are separated. They meet just above the clitoris to form Clitoral hood. They are rich in nerve supply and sensitive to erotic stimulations
Bartholin's Glands : situated in the labia minora and secret transparent slippery mucus which lubricates vaginal entrance.
Hymen : is a thin fold situated at the entrance of the vagina. It does not completely cover the entrance and permits the menstrual flow. The size, shape and texture of the hymen varies from person to person.
Clitoris : situated just above the vaginal entrance at the upper end of the labia majora. It is homologous to the penis in the male and consists of a small erectile shaft and a glans which is very sensitive. The erectile tissue hardens on erotic stimulation.
Vagina : is a fibro-muscular tube extending from the vulva to the cervix of the uterus. It is an organ of copulation accommodating erect penis and during childbirth it acts as an exit for the infant. Only lower third has nerve sensations. Recently, there have been claims that a region in the front wall of the vagina midway between the pubic bone and the cervix has a special sensitivity to erotic stimulation, called "G" spot or Grafenberg Spot.
Uterus : is a pear shaped slender and thick walled hollow muscular organ suspended in the pelvic cavity behind the urinary bladder and in front of the rectum supported by ligaments and muscles. It consists of a body, upper expanded portion above the tubal openings called Fundus and lower part called cervix.
The function of the uterus is to accommodate and nourish the growing embryo and therefore during pregnancy it undergoes the necessary changes in size and structure.
Fallopian tubes : begin at the side of the uterus extending laterally. The far end of the tubes are funnel shaped called fimbria which covers the ovaries. The tubes pick up the egg produced and released by the ovaries and serve as a meeting ground for egg and sperm.
Ovary : situated in the ovarian fossa on each side of the uterus, these are homologous to the testes in man. The ovaries have two functions: manufacturing hormones (Oestrogen and Progesterone) and producing and releasing eggs.
In each cycle, although a number of different follicles begin growing in each cycle, usually only one develops and ruptures releasing egg in a process called Ovulation.
Breasts : actually just modified sweat glands. The female breasts undergo changes in size and shape during puberty. Each breasts contains about 15-20 lobes of glandular tissues arranged in grape-like-cluster. Each lobe is drained by a duct opening into the nipple. The nipple has a rich network of nerve endings that make it highly sensitive to touch and temperature. The dark wrinkled skin of the nipple extends onto the surface of the breasts to form the areola.
Humour in sex





